Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a high precision method for manufacturing customized parts derived from a variety of different materials and within very tight tolerances. There are many benefits that come from implementing a CNC machining production solution.
Understanding CNC Machining
CNC machining is considered a subtractive manufacturing technology, which means that the end product is formed by selectively removing excess material from the workpiece. Every end-to-end CNC machining operation follows a similar four-step production process.
These four production phases are:
- Part Design
Parts produced via CNC machining generally start out as initial designs from Computer Aided Design (CAD) software. In the design phase, engineers give careful thought to all aspects of the desired final product, such as parameters for optimal performance, operating conditions for the end part, and acceptable tolerance variation levels.
- Design Conversion
Upon completion of the initial design phase, the CAD model must be converted into a functional CNC program using Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. CAM software is able to extract the geometrical requirements from the CAD model’s origin file and translate them into a CNC-compatible programming language—such as G-code or M-code—which will dictate the mechanical operations of the machine.
- CNC Machine Preparation
Next, the CNC machine operator must set up both the machine and the target material according to the specifications required by the CNC program. The operator will ensure that the correct cutting or drilling tools are properly installed and are matched with the appropriate bits or end mills. The operator must also set up the workpiece, typically either in a stationary clamp or attached directly to the CNC machine.
- Executing Programmed Operations
Finally, the CNC machine operator executes the desired mechanical processes. During operation, the CNC program precisely controls the movements of the machine tooling.
Types of CNC Machines
The most common types of CNC machines are those that use cutting tools to remove excess material from the workpiece. While there are CNC machines that employ water jet cutting and electrical discharge machining (EDM) operations, this guide will focus on the five most common categories in the following list, divided into two basic classifications: 3-axis and multi-axis machines.
3-Axis CNC Machines
3-axis machines allow cutting tools to move along straight three-dimensional vectors (up and down, left and right, forward and backward). There are two types of 3-axis CNC machines:
- CNC Milling Machines
In CNC milling operations, the workpiece remains stationary and a high-speed rotating cutting tool comes down onto the workpiece to remove excess material. This type of machine is very useful for forming basic geometric shapes.
- CNC Turning Machines (Lathes)
In CNC turning operations, the cutting tool remains stationary while the workpiece rotates at a high speed on a spindle. CNC turning offers the ability to produce cylindrical parts quickly and with tight tolerances. For example, Technox Machine and Manufacturing has CNC lathes that can produce parts with dimensions of up to 152″ in diameter and 240″ in length, while still holding tight ± 0.001″ tolerances. The big disadvantage to 3-axis turning operations is that only cylindrical parts can be manufactured efficiently.
Click here to learn more about the Differences Between CNC Milling and Turning.
Multi-Axis CNC Machines
Multi-axis CNC machines are similar to 3-axis machines, but with a higher degree of freedom in mechanical movements. For instance, multi-axis machines can employ rotational and diagonal cutting operations. There are three main types of multi-axis CNC machines:
- Indexed 5-axis CNC Milling Machines
Even though this type of milling machine can only cut along 3 linear axes during operation, in between operations the operator has the ability to rotate the bed and tool-head for the next cut, allowing for increased shaping capabilities.
- Continuous 5-axis CNC Milling Machines
This machine type allows for continuous movement along the three linear axes and two rotational axes during operation. This gives the operator the ability to create highly complex forms from the target workpiece.
- Mill-Turning CNC Centers
Mill-turning centers combine the functionalities of CNC lathes and CNC milling machines. The workpiece may be rotated at high speeds on a spindle or precisely positioned for milling operations.
Designing CNC Machined Parts – CAD Model Design
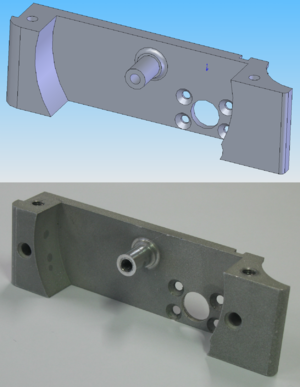
The engineer must convert the CAD model’s origin file into a CNC-compatible format, such as the open-source STEP or IGES format, or a more restricted format like IPT or SAT. It is also considered a best practice for an engineer to create a technical drawing that will be sent along with the digital CAD instructions. These drawings are used to verify design tolerances and geometries; help the machinist to identify the part’s salient features; and serve as a tangible source of verification should questions arise.
Benefits of CNC Machining
CNC machining offers several competitive advantages, including:
- Quick order lead times
- High precision
- Highly customizable
- Creates products with exceptional physical properties and performance thresholds
Materials Used
Appropriate material selection is critical for CNC machining operations. This choice is largely dependent on the expected usage for the end product. You’ll need to examine a range of material properties to determine which is best for your design, such as:
- Tensile strength
- Hardness
- Ease of operation
- Chemical resistance
- Corrosion resistance
- Thermal properties
At Technox, we utilize a broad spectrum of materials for our machining operations, including:
- Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Copper
- Bronze
- Nickel
- Cast Iron
- Inconel®
- Hastelloy®
- Plastics
CNC Machining Applications
CNC machined parts are employed in a vast array of applications across industries. At Technox, we serve a broad range of sectors, including:
- Steel
- Food and beverage
- Plastics
- Paper
- Textile
- Recycling
- Oil and gas
- Fluid power
- Construction
CNC Machined Parts at Technox
At Technox Machine and Manufacturing, we offer versatile, customized solutions to our clients and we deliver only the highest quality work. Our machining capabilities include:
If you’d like more information about the advantages of partnering with Technox, please reach out to us or request a quote.






